

In addition, the alpha helix forms a right-handed helix, while beta helix can form both right and left-handed helices. Alpha helix shows intra-molecular hydrogen bonding while beta helix shows inter-molecular hydrogen bonding. The key difference between the alpha and beta helix is the type of hydrogen bonding they show. What is the Difference Between Alpha and Beta Helix?
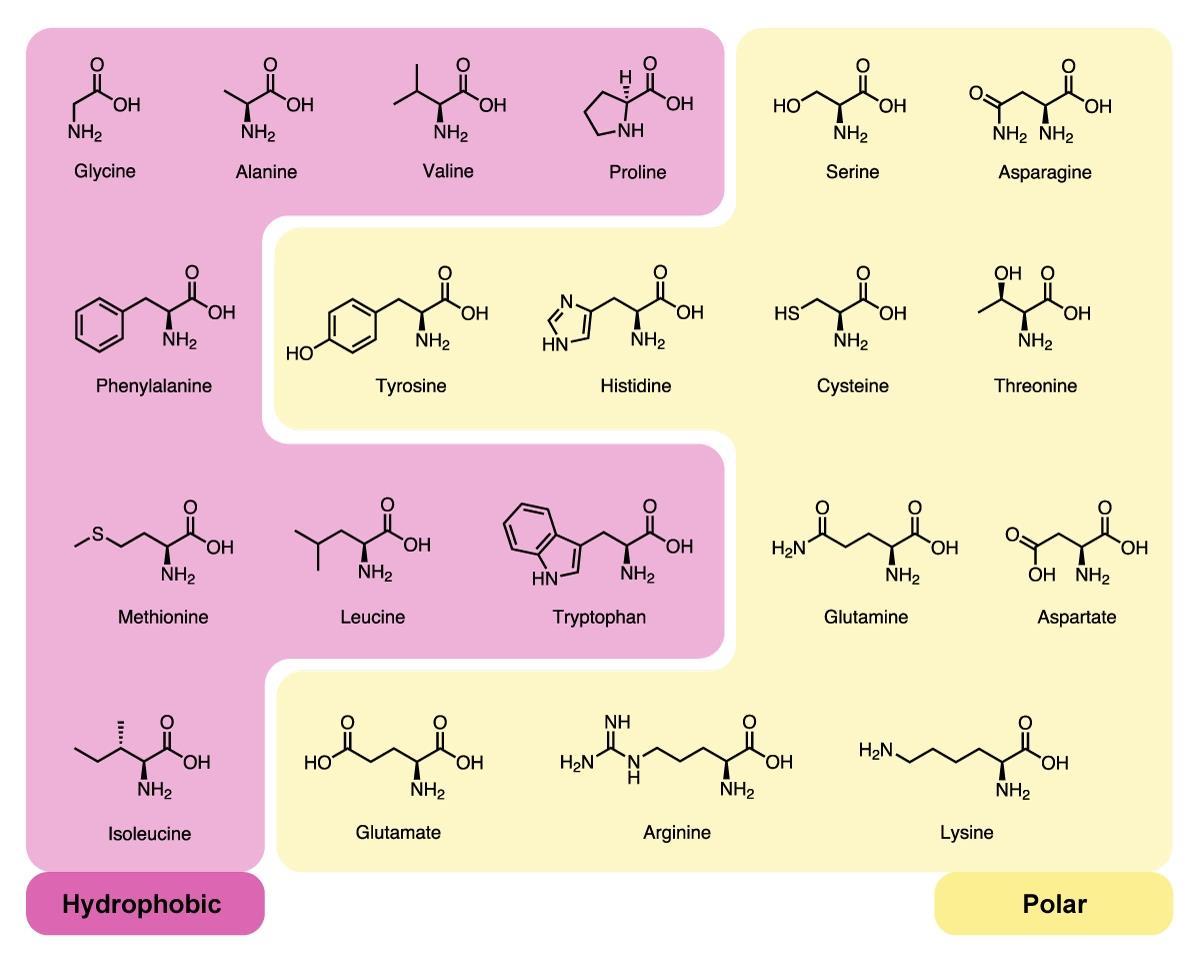
In both structures, the hydrophobicity is determined by the presence of the R groups of the amino acids.Moreover, both are stabilized by hydrogen bonds.Also, both secondary structures develop into a higher level organization.Furthermore, the chemical constituents of the alpha and beta helices are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur.Amino acids are the monomers of both secondary structures.Alpha and Beta Helix are two secondary structures of proteins.What are the Similarities Between Alpha and Beta Helix? Inter-molecular Hydrogen bonds between two sheet strands aid in the formation of a beta helix. These sheets then form into a helical structure. Formation of the beta helix takes place via two beta sheets arranged either in a parallel fashion or an anti-parallel fashion. Although it is not as common as the alpha helix, the presence of beta helices also plays a major role in protein structure. What is Beta Helix?Ī beta helix is the second most common secondary structure of a protein. Some structural proteins such as collagen and keratin are rich in alpha helices. There is an average of 3.6 residues per turn in an alpha helix as it takes 3.6 residues for the hydrogen bonds to develop. Thus, the presence of Hydrogen bonds stabilizes the structure of the alpha helix. Due to these structural characteristics, alpha helix is more resistant to mutations. In either scenario, the R groups appear to extend out of the helical structure. If the variable groups are hydrophobic, they will jut out to the hydrophobic phase of the environment. If the amino acid sequence consists of a high number of hydrophilic R (variable) groups, the R groups orient to the aqueous phase. Intra-molecular hydrogen bonds are the main cause for forming the alpha helix.Īrrangement of the alpha helix depends on the hydrophilic and hydrophobic nature of the protein. Amino acids link with each other via these peptide bonds. Here, the peptide bonds form from the amino-terminal to the carboxy-terminal. However, left-handed helices could also be present. Furthermore, the alpha helix is a right-handed helix. And, this structure appears as a rod that is wound around a central axis. Of these, the alpha helix is the commonest secondary structure of proteins. Proteins have four structural levels of organization. Side by Side Comparison – Alpha vs Beta Helix in Tabular Form Similarities Between Alpha and Beta Helixĥ. Mainly, this article focuses on the difference between alpha and beta helix. In addition, there are other secondary structures called the beta turn and hairpin structures. Therefore, there are two main secondary structures in proteins as alpha helix and beta helix. The peptide chains consist of amino acid sequences bound by peptide bonds. The secondary structures of proteins form the peptide chains in different orientations. Alpha helices form intra-molecular hydrogen bonds while the beta helices form inter-molecular hydrogen bonds.Ĭomplex proteins have four structural organizational levels – primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary. The key difference between alpha and beta helix relies on the type of Hydrogen bonding they form in developing these structures.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
